Fear of the Invisible - The Virus that never was
Fear of the Invisible is a book by Janine Roberts that takes a deep look into the world of virus isolation and vaccine manufacture. It appears that isolation of a virus is not a clean-cut business, nor is the evidence that these little fragments of information from our cells' DNA actually do cause disease.
Since the data puts the causation of polio, the flu, and even aids into doubt, the advisability of vaccination as a practice to prevent "viral diseases" loses much of its appeal as a public health measure.
The book "takes its readers on a journey into the very heart of the hunt for viruses – to the key experiments performed to prove that these invisibly small particles cause diseases that often were previously blamed on toxins or bacteria. It sheds light on the extraordinary assumptions underlying much of this research into viruses – and the resulting vaccines and antiviral medicines."From the book's Introduction
The word ‘virus' comes from the Latin for a poisonous liquid, and before that from the Sanskrit for the same. The hunt for them started when, towards the end of the 19th century, it was suggested that invisible living particles much smaller than bacteria might cause the epidemic illnesses for which no bacterial cause could be found. When the electron microscope found tiny particles in the blood serum of patients entering and leaving human cells, this was a Eureka Moment. The prediction was surely about to be proved true. These particles were assumed to be invading and hijacking our cells in order to reproduce. They were thus all condemned as poisons, as ‘viruses.'As more of these were searched for and found in sick people, many illnesses became blamed on them. They became the invisible enemy, the nano-terrorist we must fear. We were instructed that one of our first duties for our newborn children is to vaccinate them against this dreaded foe. Thus was created an ever-growing multibillion-dollar pharmaceutical industry.
As an example of what passes for virology, the science of viral illnesses, on which rests the whole edifice of a multi-billion dollar vaccine industry and the 'preventive strategy' of much of western medicine, Martin Barnes has summarized a chapter of the book that details the scientific history of polio.
You may be amazed at some of the mind boggling blunders that are at the basis of the 'science' of vaccines. But to get the full story, do buy the book and if you are able to, spread the word.
We need honesty in medicine!
- - -
Outline of the Science History of Polio
by Martin Barnes
This summary was created from information extracted from Janine Roberts' book 'Fear of the Invisible' (Impact Investigative Media Productions, 2008).
1909: Landsteiner and Popper
They ground up the spinal cord of a 9-year-old polio victim and injected a cup of the suspension directly into the brains of two monkeys. One died immediately and the other slowly became paralyzed.1910: Flexer and Lewis
Ground up human spinal cord with polio and injected the suspension directly into a monkey's brain, the monkey became paralyzed, then they extracted some fluid from its brain, and injected it into another monkey's brain, and so on through a series of monkeys paralyzing all of them in the process. But making the monkeys drink the liquid or injecting into their arms did not paralyze them.(These experiments are celebrated in modern textbooks as being the first time a 'virus' was proved to cause a major epidemic.' They could not find a bacteria in film preparations or cultures. They concluded: 'The infecting agent of epidemic polio virus belongs to the class of minute and filterable viruses that have not thus far been demonstrated with certainty under a microscope.' Toxic causes were not considered, or the shock of injecting this foreign stew directly into the brain, bypassing the immune system.)
However, the scientists were under a lot of pressure then to find a cure for the waves of polio hitting middle class kids in the summertime.
1948: Dalldorf and Sickles
Took excrement from a polio victim and prepared a 20% suspension with ether and centrifugation, then injected it directly into the living brains of suckling mice 3-7 days old. They became paralyzed.1949: Enders of Harvard claims he can make this 'virus' from human embryonic cells, making it far easier to make a vaccine.
(Their conclusion was that this was the successful isolation of a virus that must be causing polio paralysis in humans! But all they proved was that a faeces-derived suspension of human cellular material caused illness in lab animals. They called this suspension 'polio virus' and it was to become a 'vaccine seed' for modern polio vaccines. Enders receives the 1954 Nobel Prize for this!)
1950: A small ball like particle, 24-30 nm in size, was isolated from human excrement, and made visible with an electron microscope. It was named the 'polio virus.'
(Gut enteroviruses like this are very common in humans. We all have many of them.
Where was the proof this was a causative agent? Why and how would a virus found in the gut go over to attack the nervous system as polio does?)1951: Scientists report they cannot find the designated polio virus in many polio victims.
(This information was ignored. It was inconvenient. The public was demanding a solution to the polio epidemic attacking middle class kids.)
1952: Prof Konstantine Vinodouroff of the Institute of Neurology, Russian Academy of Medical Science, tells the Americans that Russia has never had an outbreak of polio. The Americans are amazed.
1954: Dr. Jonas Salk developed the first commercial polio vaccine with a virus found in 'the pooled faeces of three heathly children in Cleveland.'
(Dr. Salk did not even use the faeces from polio victims!)
The 'poliovaccine' is administered as a safety test to 400,000 US children. The official safety report stated that it protected '30-90 percent' of recipients.
(This was a vague statistic. However, manufacturers could make a 300% markup on the vaccine.)
1955: Salk distributed his vaccine 'seed' —derived from the excrement of healthy children— to manufacturers. The next step was to sprinkle it into vast quantities of minced monkey kidneys and allow the virus to multiply, then add formaldehyde to kill it. They made 27,000,000 vaccination doses.
1955: President Dwight Eisenhower awarded Salk the Congressional Medal declaring the polio vaccine a great victory for American science.
1956: Health Authorities change the rules for defining polio. Doctors are instructed to diagnose polio only if the patient has paralytic symptoms for 60 days or more. Milder cases of polio are no longer reported.
1958: CDC changes the rules for defining polio again. Cases of inflammation of the membrane that protects the brain and spinal neuron cells, causing muscular weakness and pain, but not paralysis, are no longer to be classified as polio. These cases must now be called viral or aseptic meningitis. Non-paralytic cases were now to be re-named meningitis even if the polio virus is present. The reported figures for polio were officially to exclude 'cases of aseptic meningitis due to polio virus or other entero viruses.' Reported cases of aseptic meningitis went from near zero to thousands, and polio cases dropped the same amount.
1958: Officials reduce the definition of polio again. Now all cases with classic polio paralytic symptoms are to be diagnosed initially as Acute Flaccid Paralysis (AFP). Two turds are taken from the patient and sent to the CDC to see if they can find polio in them. If not, they are declared as not polio, even if the children have all the classic symptoms.
(Making fewer cases of polio by changing the definition was a fraudulent way to make it seem like the polio vaccinations were working.)
1958: Officials triumphantly declared large parts of the world polio free, even while the newly defined Acute Flaccid Paralysis (AFP) suddenly became common. Credit for this great victory over disease was given to Salk, Sabin and the vaccine manufactures.
Report in JAMA Feb 25, 1961: "It is now generally recognized that much of the Salk vaccine used in the U.S. has been worthless." Live strains produced by Sabin and put in sugar cubes were adopted instead.
2008: Ordinary doctors still do not have the power to diagnose polio by observing symptoms. The World Health Organization still demands that two turds from each victim of infantile paralysis be sent to their laboratories. If no polio virus is found in these, the cases are declared not to be polio, even if these children are suffering from the same severe paralysis symptoms and pain as found in the worst cases of polio during the American epidemics.
Question: Could something else be causing polio besides the virus? Finding the polio virus in human excrement is natural, and finding it there does not prove it causes polio, symptoms of paralysis in the motor neuron cells of the backbone.
2008: On the CDC website Dr. John Lienhard explains that too much hygiene was the cause of the polio epidemics. Most kids pick up the virus in garden soil and become naturally immune to it, but not the kids subjected to the overly hygienic parents of the 50's.
Conclusion: The effectiveness of the Salk vaccine (and Sabin live vaccine in sugar cubes) is something that we have all come to accept, but it is nothing more than a scientific myth, fraudulently promoted by the political and medical authorities of the time, and still believed today. Millions of polio vaccine injections are still given worldwide every year for essentially no purpose. Causation by a virus has not been shown.
The Case for Toxins Causing Polio1824: Metal workers had suffered for centuries from a paralysis similar to polio caused by the lead and arsenic in the metals they were working with. English scientist John Cooke observed: 'The fumes from these metals, or the receptance of them in solution into the stomach, often causes paralysis.'
1890: Lead arsenate pesticide started to be sprayed in the US up to 12 times every summer to kill codling moth on apple crops.
1892: Polio outbreaks began to occur in Vermont, an apple growing region. In his report the Government Inspector Dr. Charles Caverly noted that parents reported that some children fell ill after eating fruit. He stated that 'infantile paralysis usually occurred in families with more than one child, and as no efforts were made at isolation it was very certain it was non-contagious' (with only one child in the family having been struck).
1907: Calcium arsenate comes into use primarily on cotton crops.
1908: In a Massachusetts town with three cotton mills and apple orchards, 69 children suddenly fell ill with infantile paralysis.
1909: The UK bans apple imports from the States because of heavy lead arsenate residues.
1921: Franklin D. Roosevelt develops polio after swimming in Bay of Fundy, New Brunswick. Toxicity of water may have been due to pollution run-off.
1943: DDT is introduced, a neurotoxic pesticide. Over the next several years it comes into widespread use in American households. For example, wall paper impregnated with DDT was placed in children's bedrooms.
1943: A polio epidemic in the UK town of Broadstairs, Kent is linked to a local dairy where cows were washed down with DDT.
1944: Albert Sabin reports that a major cause of sickness and death of American troops based in the Philippines was poliomyelitis. US military camps there were sprayed daily with DDT to kill mosquitos. Neighboring Philippine settlements were not affected.
1944: NIH reports that DDT damages the same anterior horn cells that are damaged in infantile paralysis.
1946: Gebhaedt shows polio seasonality correlates with fruit harvest.
1949: Endocrinologist Dr Morton Biskind, a practitioner and medical researcher, found that DDT causes 'lesions in the spinal cord similar to human polio.'
1950: US Public Health Industrial Hygiene Medical Director, J.G. Townsend, notes the similarity between parathion poisoning and polio and believes that some polio might be caused by eating fruits or vegetables with parathion residues.
1951: Dr. Biskind treats his polio patients as poisoning victims, removing toxins from food and environment, especially DDT contaminated milk and butter. Dr. Biskind writes: 'Although young animals are more susceptible to the effects of DDT than adults, so far as the available literature is concerned, it does not appear that the effects of such concentrations on infants and children have even been considered.'
1949-1951: Other doctors report they are having success treating polio with anti toxins used to treat poisoning, dimercaprol and ascorbic acid. Example: Dr. F. R. Klenner reported: 'In the poliomyelitis epidemic in North Carolina in 1948 60 cases of this disease came under our care... The treatment was massive doses of vitamin C every two to four hours. Children up to four years received vitamin C injection intramuscularly... All patients were clinically well after 72 hours.'
1950: Dr. Biskind presents evidence to the US Congress that pesticides were the major cause of polio epidemics. He is joined by Dr. Ralph Scobey who reported he found clear evidence of poisoning when analyzing chemical traces in the blood of polio victims.
Comment: This was a no no. The viral causation theory was not something to be questioned. The careers of prominent virologists and health authorities were threatened. Biskind and Scobey's ideas were subjected to ridicule.
1953: Clothes are moth-proofed by washing them in EQ-53, a formula containing DDT.
1953: Dr. Biskind writes: 'It was known by 1945 that DDT was stored in the body fat of mammals and appears in their milk... yet far from admitting a causal relationship between DDT and polio that is so obvious, which in any other field of biology would be instantly accepted, virtually the entire apparatus of communication, lay and scientific alike, has been devoted to denying, concealing, suppressing, distorting and attempts to convert into its opposite this overwhelming evidence. Libel, slander, and economic boycott have not been overlooked in this campaign.'
1954: Legislation recognizing the dangers of persistent pesticides is enacted, and a phase out of DDT in the US accelerates along with a shift of sales of DDT to third world countries.
(Note that DDT is phased out at the same time as widespread polio vaccinations begin.)
1962: Rachel Carson's Silent Spring is published.
1968: DDT registration cancelled for the US.
2008: Acute Flaccid Paralysis (AFP) is still a raging, but little mentioned, epidemic in many parts of the world where pesticide use is high, and DDT is still used.
2008: WHO states on its website: 'There is no cure for polio. Its effects are irreversible.'
Conclusion: Modern belief that polio is caused by a virus is an ongoing tragedy for the children - poisoning victims - involved. Public funds are wasted on useless and dangerous vaccines when the children could be treated with antitoxins.
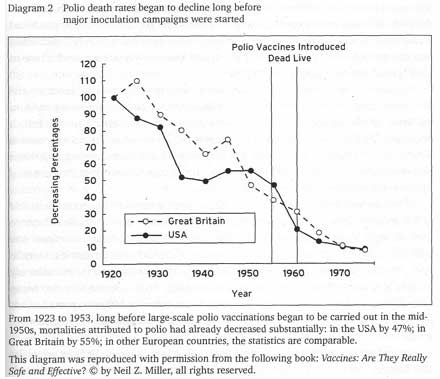
This graph shows that polio death rates were already in steep decline when polio vaccines were started. This directly throws into question the effectiveness of the vaccines.Martin K. Barnes
www.maisondemartin.com- - -
See also:
posted by Sepp Hasslberger on Tuesday November 25 2008
updated on Thursday November 27 2008URL of this article:
http://www.newmediaexplorer.org/sepp/2008/11/25/fear_of_the_invisible_the_virus_that_never_was.htm
Related ArticlesNigeria: Polio Vaccine Found Contaminated
As the World Health Organization is pushing to eradicate polio by increasing vaccination in a concerted drive, some of the local State authorities in Nigeria were contesting the drive, based on rumors of contamination, specifically an anti-fertility type substance supposed to be in the vaccines. Polio vaccination has been under fire before in Africa. KIHURA NKUBA, an African radio broadcaster has documented the Ugandan polio scandal. The vaccine used there... [read more]
March 10, 2004 - Sepp HasslbergerPolio Vaccine Voodoo - Intriguing Questions
"The World Health Organization announces a push to eradicate polio", we are told in big headlines, and we assume that polio may be on its way out for good. But the story is really that the health ministers of six countries - Nigeria, India, Pakistan, Afghanistan, Niger and Egypt - have agreed to give vaccination against polio in their respective countries a big push. There is plenty of controversy, to... [read more]
January 25, 2004 - Sepp Hasslberger